The UAE is introducing e-invoicing as part of its efforts to modernize tax compliance and drive digital transformation. This initiative is a significant step toward improving efficiency, reducing errors, and aligning business processes with international tax and trade standards.
With governments worldwide adopting digital invoicing to enhance transparency and streamline tax reporting, the UAE has developed a structured e-invoicing framework. Businesses operating in the country will need to comply with the new requirements to ensure seamless transactions and avoid penalties.
Why is the UAE Implementing E-Invoicing?
The introduction of e-invoicing is part of the UAE’s long-term strategy to enhance regulatory compliance and simplify tax administration. Some of the key benefits include:
- Standardization and Accuracy – Ensures consistency in invoice formats and minimizes errors.
- Improved Tax Compliance – Reduces tax fraud and enhances oversight by regulatory authorities.
- Business Efficiency – Automates invoicing processes, reducing paperwork and manual work.
- Global Alignment – Supports international trade by adopting widely accepted digital invoicing standards.
By implementing e-invoicing, the UAE aims to create a more transparent and efficient tax environment that benefits businesses and regulators alike.
How Does the UAE’s E-Invoicing Model Work?
The UAE has adopted the Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control and Exchange (DCTCE) model for e-invoicing. This model is a 5 Corner model that ensures invoices are processed and validated in real-time, thereby enhancing data security and compliance.
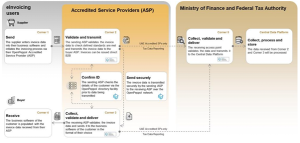
Key aspects of the system include:
- Businesses must generate and exchange invoices digitally in a standardized format.
- Transactions are validated instantly, reducing discrepancies and tax compliance risks.
- The system is designed to prevent fraud while ensuring smooth cross-border trade.
By adopting this approach, the UAE is creating a digital tax ecosystem that supports business growth while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Who Needs to Comply with E-Invoicing Regulations?
E-invoicing applies to all businesses operating in the UAE, regardless of their VAT registration status. This includes:
- VAT-registered businesses – Required to issue structured e-invoices for all taxable transactions.
- Non-VAT registered businesses – Must also generate electronic invoices, ensuring their transactions are recorded and compliant.
The goal is to integrate all business activities into a unified tax reporting system, reducing tax evasion and improving financial transparency.
Types of E-Invoices Covered Under the New Regulations
The UAE’s e-invoicing framework applies to various types of business transactions, including:
- Tax Invoices – Issued for standard B2B and B2G transactions.
- Commercial Invoices – Used for non-taxable transactions.
- E-commerce and Export Invoices – Required for online sales and cross-border transactions.
- Credit Notes – Must reference original invoices to document adjustments or returns.
It is important to note that eInvoicing for B2C transactions is not yet incorporated into the eInvoicing framework.
What Information Must Be Included in an E-Invoice?
To adhere to UAE e-invoicing regulations, the essential data fields mandated for a standard tax e-invoice (XML) under UAE PINT regulations are organized into six distinct sections:
- Invoice Details – Basic invoice information, including invoice number, date, type, currency, transaction type, and payment-related details.
- Seller Details – Information about the seller, including name, address, tax identifiers, and registration details.
- Buyer Details – Information about the buyer, including name, address, and tax identifiers.
- Document Totals – Summarizes invoice amounts, including total amounts with and without tax, tax amounts, and amount due.
- Tax Breakdown – Details about tax categories, taxable amounts, tax amounts, and tax rates.
- Invoice Line – Detailed information on each invoiced item, including descriptions, quantities, prices, and tax details.
The list outlines the 50 key fields necessary for a standard tax e-invoice (XML) in compliance with UAE regulations, aligning with both VAT laws and PEPPOL International Invoice (PINT) standards. Among these, 15 fields mandated by UAE PINT are not currently addressed under UAE VAT law.
Aligning with Global Standards
The UAE’s e-invoicing model follows international best practices to ensure compatibility with global trade and taxation systems. It incorporates:
- PEPPOL Standards – Used for business interoperability in international trade.
- ISO Invoice Standards – Ensuring consistency in invoice structure and content.
- Global Tax Codes – Facilitating seamless tax reporting for multinational businesses.
By aligning with these standards, UAE businesses can engage in cross-border transactions more efficiently and remain competitive in the global market.
Special Considerations for Specific Transactions
Different industries and transaction types may have unique invoicing requirements. Businesses involved in exports, Free Trade Zones, and e-commerce must ensure that their invoices comply with sector-specific rules. This includes:
- Export invoices requiring designated transaction codes.
- Free Trade Zone invoices with special VAT treatment fields.
- E-commerce invoices that include mandatory delivery and tax details.
- Credit notes that must reference original invoice details.
Understanding these requirements is essential for businesses to maintain compliance and avoid disruptions.
Preparing for the Transition to E-Invoicing
Businesses must take proactive steps to ensure compliance with the new regulations. Key actions include:
- Upgrading invoicing systems to generate compliant e-invoices.
- Training finance and accounting teams on e-invoicing standards.
- Integrating digital solutions that automate invoicing and tax reporting.
- Staying updated on evolving FTA regulations to ensure ongoing compliance.